Buf Schema Registry repositories provide a platform for sharing your Protobuf schemas with your team, customers, or the wider Buf community.
While roughly analogous to Git repositories, a Buf repository is only a remote location—there is no concept of a repository "clone" or "fork". Repositories do not exist in multiple locations.
Every repository is identified by its module name, allowing it to be imported by other modules and uniquely identified within the BSR.
Many organizations with public Protobuf files are already using the BSR, and some bigger ones are officially maintained by Buf. These include:
- cncf/xds
- envoyproxy/envoy
- envoyproxy/protoc-gen-validate
- gogo/protobuf
- googleapis/googleapis
- grpc/grpc
- opencensus/opencensus
- opentelemetry/opentelemetry
To push Buf modules to the Buf Schema Registry, you can use the buf push command. A single
Buf Schema Registry repository is capable of containing multiple versions of Buf modules, which are stored as commits and tags.
Creating a repository
To create a new repository, you can log in to the Buf Schema Registry, click on Show all under the "Your repositories" section, and then select Create Repository.
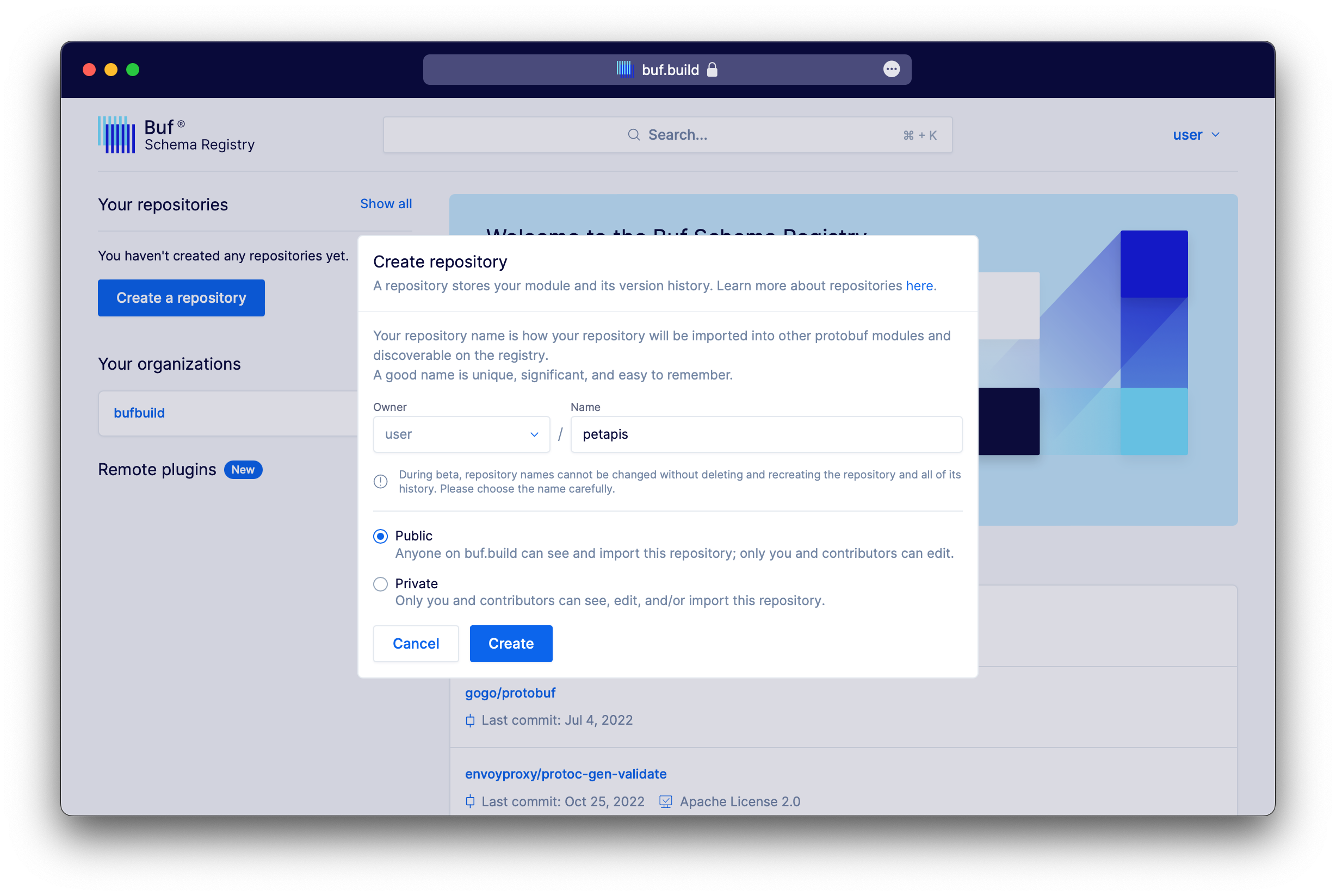
When setting up a new repository, there are a few important things to keep in mind:
- The repository name must be unique within its namespace and can be between 2 and 255 characters in length. It can only contain lowercase letters, numbers, or hyphens (-).
- Once you have created the repository, you can use the
buf pushcommand to begin pushing modules to it. - You have the option to link a source code URL later in the repository settings.
- Additionally, you can also provide a description of the repository, which can be up to 350 characters in length.
You can't rename a Buf Schema Registry repository once it's created.
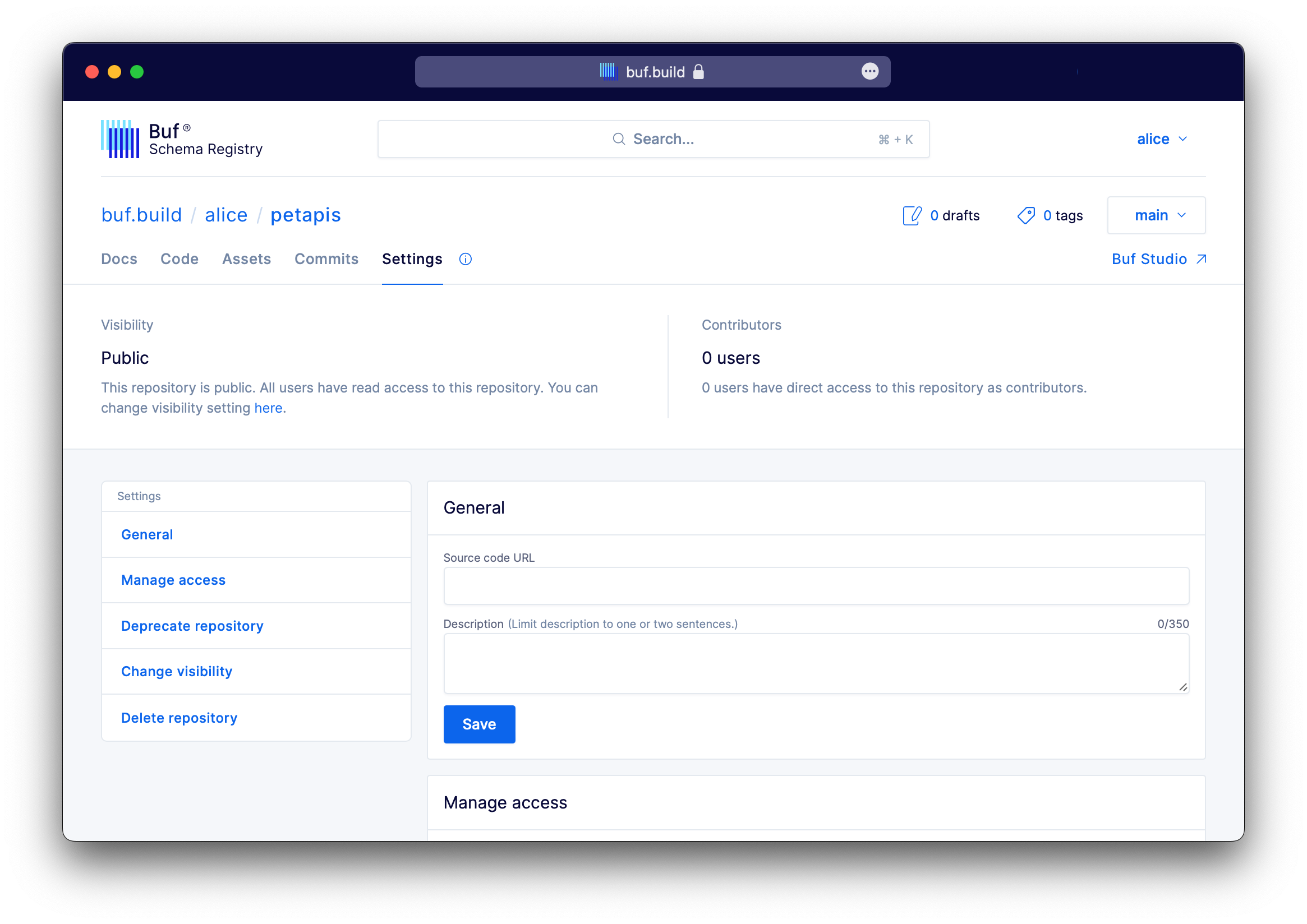
Creating a private repository
To create a private repository, navigate to Buf Schema Registry and select Repositories and Private.
To update your public repository to private, navigate to your repository, select Settings and Change Visibility.
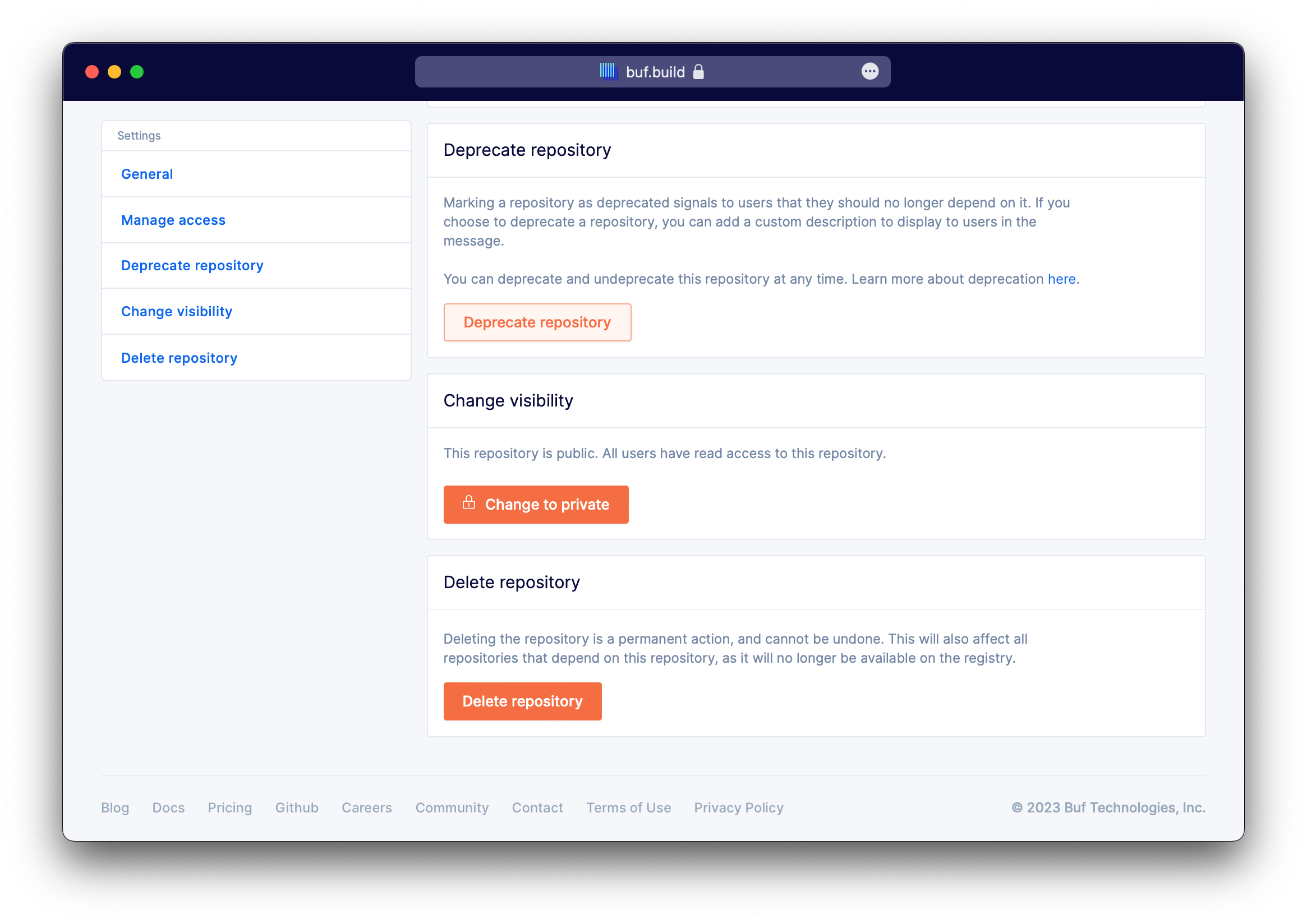
Deleting a repository
-
Navigate to Buf Schema Registry and select Show all under "Your repositories".
-
Select a repository from the list, select Settings, and then Delete Repository.
Deleting a repository deletes all the images it contains and its build settings. This action cannot be undone.
Pushing a Buf module to Buf Schema Registry
Before you can push a module to the Buf Schema Registry, you need to assign a name to your local module that corresponds with the name of the repository you created on the Buf Schema Registry website.
Name your local modules using one of these methods:
- When you create them, using
buf mod init <remote>/<owner>/<repository_name> - By re-naming an existing local module
buf.yaml
version: v1 name: <remote>/<owner>/<repository_name>
Now you can push this repository to the registry.
$ buf push
Once the module is uploaded, it will be readily available for your team or community to use.
Deprecate or undeprecate a repository
BSR repositories can be deprecated. buf warns you when you run buf mod update on a module that depends on a
deprecated repository.
You can deprecate a repository with
$ buf beta registry repository deprecate <buf.build/owner/repository> [--message <deprecation message>]
Undeprecate a deprecated repository with
$ buf beta registry repository undeprecate <buf.build/owner/repository>
Update the visibility of a repository
The visibility of BSR repositories can be updated.
You can update the visibility with
$ buf beta registry repository update <buf.build/owner/repository> --visibility [public,private]
The --visibility flag must be one of: private or public.